“What is skew in English?” is a question that often arises when discussing data analysis and statistics. In its simplest form, skew refers to a distortion or unevenness in data. Imagine taking a straight line and bending it—that’s essentially what skewing does to data, changing its original shape and potentially leading to inaccurate conclusions. This distortion can occur due to various factors, such as biased sampling, incomplete information, or even accidental errors. Think of it like a company’s results being affected by last-minute changes, causing them to be skewed and not accurately reflecting the true picture. Understanding skew is crucial for making informed decisions based on data, ensuring that your analysis is reliable and reflects the reality of the situation.
What is Skew in English? A Distortion of Data
In the realm of data analysis, the term “skew” represents a distortion or deviation from a symmetrical distribution. Imagine a perfectly balanced seesaw, with equal weight on both sides. This is analogous to a symmetrical distribution. However, when we introduce skew, we tip the seesaw, creating an imbalance. This imbalance is precisely what “skew” signifies in the context of data.
Skew occurs when data points are unevenly distributed, with a concentration on one side of the distribution. This can result in a skewed mean, which is an inaccurate representation of the central tendency of the data.
To understand skew better, let’s visualize it. Consider a bell-shaped curve, known as a normal distribution. In a normal distribution, the data is symmetrically distributed around the mean, with an equal number of data points on either side. However, when skew is present, the bell curve is distorted.
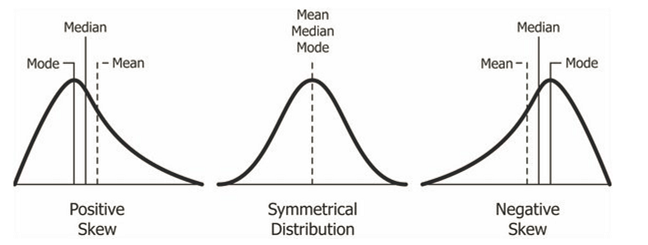
Skew can be either positive or negative:
- Positive skew means that the tail of the distribution is longer on the right side, indicating a concentration of data points towards the lower end of the scale.
- Negative skew, on the other hand, has a longer tail on the left side, indicating a concentration of data points towards the higher end of the scale.
Understanding skew is crucial for accurate data analysis and interpretation. If you’re working with skewed data, it’s essential to be aware of the potential distortion and its implications for your results.
What is Skew in English? A Twist in Data
Think of skew as a metaphorical wrench that twists data, altering its original form. When data is skewed, it means its distribution is uneven, creating a lopsided picture of reality. Imagine a pie chart representing different age groups in a population, but one age group takes up a disproportionately large slice. This creates a distorted view of the population’s age distribution. Here are some key points to consider:
- Skewed data can lead to misinterpretations. If we base our understanding of a phenomenon on skewed data, our conclusions might be inaccurate.
- Skewed data can be deliberate or accidental. Sometimes, the distortion is intentional to manipulate perception. Other times, it results from errors in data collection or analysis.
What is Skew in English? A Deviation from Accuracy
When data is skewed, it means it’s deviating from what’s considered accurate or representative. It’s like having a scale that’s slightly off, giving you a slightly wrong weight. Imagine a survey asking people about their favorite color. If the survey only included people from one city, the results would be skewed because they don’t reflect the preferences of people from other cities. This kind of skew happens when the data collection method is flawed, like:
- Biased Questions: Questions that lead people to answer in a specific way. For example, “Do you agree that the government should invest more in healthcare?” is a leading question.
- Incomplete Data: Missing information or data that is not collected properly. For instance, a survey that only considers people with a certain income level would have incomplete data.
- Sampling Errors: When the sample of people chosen to represent a group doesn’t accurately reflect the whole population. A survey that only includes people from one age group would have a sampling error.
Skewed data can lead to incorrect conclusions and decisions. So, it’s important to be aware of the potential for skew when analyzing data and to take steps to minimize it.
| Cause of Skew | Description |
|---|---|
| Biased Questions | Questions that lead people to answer in a specific way. For example, “Do you agree that the government should invest more in healthcare?” is a leading question. |
| Incomplete Data | Missing information or data that is not collected properly. For instance, a survey that only considers people with a certain income level would have incomplete data. |
| Sampling Errors | When the sample of people chosen to represent a group doesn’t accurately reflect the whole population. A survey that only includes people from one age group would have a sampling error. |
What is Skew in English? A Misalignment of Truth
Imagine a perfectly balanced scale, with equal weights on each side. When data is skewed, it’s like adding extra weight to one side, tipping the balance and giving a distorted view of the truth. Skewed data misrepresents the reality of a situation, making it difficult to draw accurate conclusions. It’s like seeing a photo with a tilted frame – the perspective is off, and the image doesn’t reflect the true scene.
This distortion can occur in various ways:
- Biased sampling: When the selection of data points favors a specific group, the results may be skewed towards that group’s characteristics.
- Measurement errors: Inaccurate measurements or recording methods can introduce skew into the data, leading to misleading results.
- Outliers: Extreme values that are significantly different from the rest of the data can skew the average and create a misleading picture of the overall trend.
Therefore, understanding skew is crucial for making informed decisions based on data. Recognizing and correcting skewed data helps ensure that our analysis and interpretations are grounded in reality, leading to more accurate and reliable conclusions.
What is skew in English? Conclusion
Understanding “What is skew in English?” is essential for anyone working with data. Skew refers to a distortion in data, making it uneven and potentially misleading. It’s crucial to be aware of skew’s presence, its causes, and its impact on our interpretation of data. While skew can be intentional, it often arises due to sampling biases, measurement errors, or outliers. In such cases, acknowledging and addressing the skew becomes vital to ensure that our conclusions are grounded in reality.
By understanding the concept of skew, we can critically evaluate data, identify potential distortions, and take steps to minimize their influence. This allows us to make more informed decisions, ensuring that our analysis reflects the truth and not a skewed version of reality.
What is skew in English? Quick FAQ
How does skew affect data analysis?
Skew distorts the true picture presented by data. It can lead to misinterpretations and inaccurate conclusions. For instance, a skewed sample might give a false impression of the average income in a city. If you’re making decisions based on skewed data, you might end up with faulty results.
What are some examples of skewed data?
Think of a survey asking about people’s favorite ice cream flavor. If the survey was only conducted in a city known for its artisanal ice cream shops, the results would be skewed towards those flavors. Another example is a product review website that only displays positive reviews – this skews the perception of the product’s quality.
How can I identify if data is skewed?
Look for uneven distributions, extreme values (outliers), or a concentration of data points on one side of the distribution. You can also analyze the mean, median, and mode of the data to see if they significantly differ. These discrepancies can be indicators of skewed data.
